Windows Desktop: Icons, Folders and Taskbar
 Activity
Handout One: Windows - Basic Operations
Activity
Handout One: Windows - Basic Operations
On: Turning your computer on is done in the usual manner. Push the larger button on the front of the box encasing the computer. If the monitor screen shows a “Signal Missing” message, it means that although the monitor has been turned on, the CPU power has not yet been turned on; simply turn it on. Your computer may take a few minutes to complete the "booting" up of power to build the "desktop" that shows you icons or symbols of what is on your computer.
Off: Do not simply turn the CPU (central processing unit - your computer) off. The CPU is the engine or brain of the computer. The shut down function is vital, especially if you are on a network. Before you turn off the power and screen, click on Start - a button in the lower left corner of the screen. Using the mouse, slide the pointer to highlight the words, "Shut Down" and left click. The Shut Down Windows dialogue box outlining four choices will appear. Click on the button for the option you want, then click on the Yes button.
Windows is Microsoft’s operating system for IBM compatible personal computers (PCs) which simply means that it is the interface between you and the software programs you use; such as word processing (Claris Works, Microsoft Word or Corel Word Perfect), spreadsheets (Excel or Lotus), database (FoxPro, Endnote, or FileMakerPro), Internet connection software (Telnet, FTP). It is a graphic user interface, requiring the use of a mouse.
Your PCs Windows operating system has many built-in utilities, such as disk and file management; and handles many internal functions, such as memory allocation. Windows also comes with several built-in accessory programs (or little applications-“applets”); a basic word processor (Word Pad), a ClipArt gallery, and a simple drawing program (Paint), to name a few.
There are three main visible parts
to the screen: The Desktop, Icons, Taskbar.
Desktop: Large open area
of your computer screen comparable to your physical desk; when you have
mastered the basics, you can organize the Windows desktop to suit your
needs.
Icons: Pictures or graphic
symbols which represent actions or files. Three of the icons you will see
on Windows systems are: My Computer, Network Neighborhood, and Recycle
Bin.
Taskbar: At the bottom of
the screen, with Start in the left corner and other icons in the right
corner, this bar displays all programs currently running.

Windows Desktop: Icons, Folders and Taskbar
Windows assumes that you are right-handed and uses the mouse device to select, activate, move, de-select or otherwise manipulate its components. (If you are left-handed, you can switch the left and right mouse buttons via the Control Panel). As you move the mouse around on the mouse pad, notice how the pointer moves on the screen. If you run out of room, pick up the mouse and place it on another spot on your mouse pad.
There are five basic actions you
can perform using the mouse: point, left click, left double click,
drag and drop, and right click.
1. Point: Slide the mouse
until the tip of the pointer is on the item you want to point to.
2. Left Click: Press and
release the left mouse button once (also Select).
3. Left Double Click: Leaving
the pointer on the item, quickly press and release the left mouse button
twice (also Open).
4. Drag and Drop: Point to
the object to be dragged, press and hold down the left or right mouse button;
keeping the button pressed, slide the mouse (dragging the item along) until
the item (or window border) is at its new location; now release the mouse
button.
5. Right Click: Point and
click with the right mouse button.
At a very slightly advanced level, the
mouse and control key (Ctrl) on the keyboard can be used to select multiple
items, either one by one or by drawing a box around them.
Note: Clicking on an item is also
called selecting; to de-select, move the mouse so that the pointer is on
an empty area of the desk top and left click once.
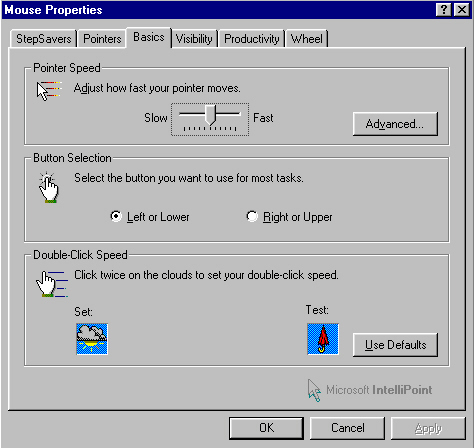
Setting Mouse Properties
Exercise: Go
to Start. Try the Shut Down function, but click on Cancel in the Dialogue
Box.
Exercise: Locate
the FirstClass icon on the Desktop. Go to Start. Login to your email account.
Your computer has a number of items that
may be helpful to you. They are found in a section of the computer called
Accessories.
Take a tour by going to Start - Programs
- Accessories. You will find the items listed by categories like Communications,
Entertainment and Games. If there is an arrowhead beside the item, click
on it to see an extended menu.
Exercise: Using the Calculator
Go to the Start button in the lower left
corner of your desktop.
Go to Programs/Accessories/Calculator
- a calculator will appear on the desktop.
Add the following numbers: 352+673
Subtract these numbers: 987-42
Close the calculator
Exercise: In Accessories go to games. Open solitaire.
Your computer has a built in calendar and clock. This is usually set when you get your computer and you will receive alerts when the time is changing for daylight savings time. There is a small battery inside the hard drive case running this utility. You may need to reset the time or date. You will find this item by clicking your right mouse button on the time shown in the lower right corner of the desktop.
Exercise: Changing the time on your computer
Go to the right corner of the desktop and
click the right mouse pointer over the time shown there.
Select Adjust time/date from the menu
Set the clock to the correct time.
Find the correct date on the calendar.
Click Apply and OK
Exercise: Create a Shortcut to the Windows Accessory, NotePad.
Exercise:
Use Help.
Go to Start and click on the Help option.
Click on the link "How to Use Help" on
the Contents tab.
Next, click on "Find a Topic" and read
the instructions in the right hand section of this window.
Now click on the tab for Index and scroll
through the topics listed there. Try typing "printing" into the keyword
find box.
Scroll through the items listed on printing.
Choose an item you want to know more about.
Read what the help program tells you about
this item.
Top of Page